Function Name |
XML Data Source | ||||||
Category |
XML | ||||||
Icon |
 |
||||||
Description |
Define the XML source data for mapping | ||||||
Inputs |
|
||||||
Outputs |
|
||||||
Properties |
|
||||||
Usage
Allows XML documents to be used as a data source within the Data Mapper.
Inputs
The component has 2 inputs, 'Filename' and 'XML String', only one of these can be used at a time (you can only connect one of them within a given transform).
If the 'Filename' input is connected then the value read from the connector will be treated as the filename for the XML document to load (if the connector provides a sequence of filenames, then multiple XML documents are loaded).
If the 'XML String' input is connected then the value read from the connector will be treated as raw XML data and loaded into the document (if the connector provides a sequence of values, then each is treated as a separate XML document and multiple documents are loaded).
If neither of the inputs are connected then the filename is taken from the default filename (accessible via the properties window).
Creating an XML data source
To begin, drag the XML Source component from the XML section of the Component Palette onto a new Data Mapper file.

As soon as you drag the component over, the XML Source Wizard will open, guiding you through the process of defining your mapping source.
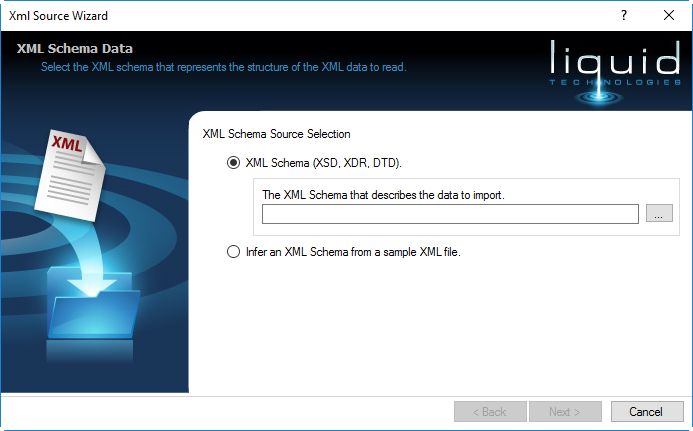
You need to provide a schema to describe the data that you will be mapping, you can do this using by providing an XSD, DTD or XDR.
If you don't have a schema (i.e. you just have an xml data file) then you can infer a schema from the XML data file (see Inferring an XML Schema (XSD)).
If you infer an XSD from an XML document, then you may have to finesse the XSD manually in the XSD Editor.

The second page contains options relating to the inferring process.
Schema Name
The name of the schema that will be produced (there is no need to add the .xsd extension).
If more than 1 schema file needs to be created, then the schema files will be named <Schema Name>1.xsd, <Schema Name>2.xsd etc
Output Directory
The location where your schema file/files will be written.
Encoding
The encoding that will be applied to your XML Schema (UTF-8 or UTF-16 are the most commonly used, only change this if you understand encoding).
Occurrence Options
If the Occurrence property is set to Restricted, the first time elements are encountered in the XML document, the schema declaration is inferred as minOccurs="1".
When attributes are encountered, the schema declaration is inferred as use="required". If the Occurrence property is set to Relaxed, element schema declarations are inferred as minOccurs="0", and attribute schema declarations are inferred as use="optional".
Type Inference Option
If the TypeInference property is set to Relaxed, the inferred type of elements and attributes in the XML document with simple content is always xs:string.
If the TypeInference property is set to Restricted, more specific types are inferred, such as xs:date, xs:decimal, xs:unsignedByte, and so on.

When you have selected a Schema, the next part of the Wizard will allow you to select the root element or complex type.
Types that are abstract are disabled and grayed out.

The next section allows you to specify where you want your source data to come from. This is the data that will be mapped when your transform executes. If you inferred a Schema from source XML, you may wish to use this here. If you specified an XSD you already had before starting your mapping project, you can use it to generate default XML data to use in the Mapper.
Properties
You can alter the Properties of an XML Reader in the Mapper by right-clicking it and choosing Show Properties. These properties can all be set in the Wizard when you add a Source Data component to the Mapper, but if you need to alter any of them you can do so here.

The General tab allows you to alter the name of the component within your mapping project.

The Structure tab allows you to select a Schema, root element and type for your source data, as well as instructing the Mapper to validate the Schema when it loads it.

The Source Data tab allows you to select a file to use as source data when the Mapper executes.
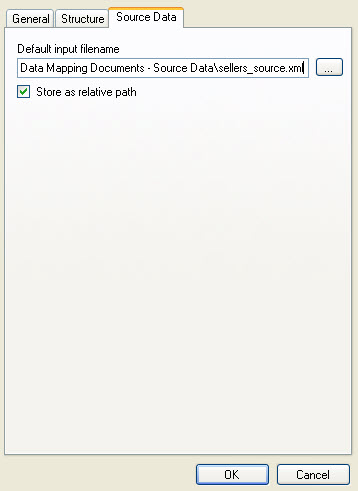
Examples
Now your XML Source Data component should appear in the Mapper as the XML Reader.

You can click to expand and collapse items in the XML Reader as it appears in the Mapper.

You can make connections between the XML Reader and XML Writer once you have them both imported, by clicking and dragging between items.

These connections define which data items in the source are mapped to items in the target.
