Function Name |
Greater Than | ||||
Category |
Comparator | ||||
Icon |
 |
||||
Description |
Determine whether one value is greater than another | ||||
Inputs |
|
||||
Outputs |
|
||||
Properties |
|
||||
Usage
The Data Mapper Comparator Greater Than function allows you to determine whether one value is greater than another. The values in question may be from the input data source or components within the Mapper, such as Constants or function outputs. Since the Greater Than function outputs a boolean value, it is most usefully used in conjunction with other functions such as Set, Aggregate and Logic components. To apply the Comparator Greater Than function, use the following process:
Create a new Data Mapper file, dragging your XML data source and targets into the editor area. For this example we are using staff_source.xsd, an XML Schema Definition inferred from the following source:
| Source XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<staff> <employee> <first_name>Mark</first_name> <second_name>Brown</second_name> <started>2001</started> <permanent>true</permanent> </employee> <employee> <first_name>Jane</first_name> <second_name>Jackson</second_name> <started>1998</started> <permanent>true</permanent> </employee> <employee> <first_name>Joe</first_name> <second_name>Simpson</second_name> <started>2008</started> <permanent>false</permanent> </employee> <employee> <first_name>Lynn</first_name> <second_name>Nicolson</second_name> <started>2008</started> <permanent>false</permanent> </employee> </staff> |
|
For our target schema we will be using staff_target.xsd, inferred from the following XML:
| Target XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<company> <staff_member since="2000" contract="false"> <f_name>Ken</f_name> <s_name>Jones</s_name> </staff_member> <staff_member since="2003" contract="true"> <f_name>Linda</f_name> <s_name>Lee</s_name> </staff_member> <staff_member since="1998" contract="false"> <f_name>Paul</f_name> <s_name>Mitchell</s_name> </staff_member> </company> |
|
The data models employees within an organisation. Let's assume that, rather than mapping all data values, we only want to map "employee" elements representing staff members with surnames within the second half of the alphabet - whose "second_name" values start from "N" to "Z". Here is the Data Mapper with Source and Target imported:

Drag the Comparator Greater Than function from the Component Palette into the mapping area:


The Greater Than function takes two inputs representing the values you want to compare. The function output will indicate true if Value 1 is greater than Value 2, and false if it is not (including if the values are equal). Both inputs and output of the Greater Than function may be connected to items in the XML Reader/ Writer or other components in the Mapper.
Since we want to map only elements whose "second_name" value comes from the second half of the alphabet, connect its output in the XML Reader to the Value 1 input in the Greater Than function.

Now we need to define the value to compare the input surname to. Drag a Constant Value from the Data Type section onto the Mapper. Right-click it and choose Show Properties. Enter a String as the Data Type and "N" as the value.
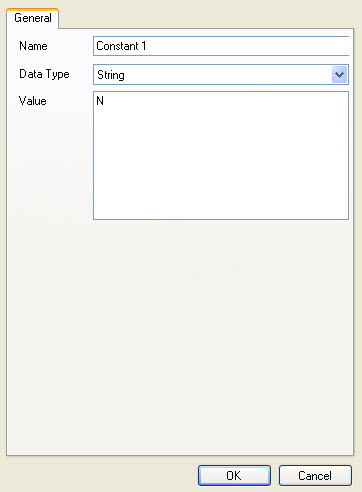
Connect the Constant output to the Value 2 input in the Greater Than function.

Now each time the Mapper encounters the "second_name" element, it will check whether the name is after "N" in the alphabet (which includes names starting with "N"). If a name is greater than "N", the function will output a value of true, otherwise it will output a value of false. Let's now use this information to filter our data. Drag a Filter function from the Set section onto the Mapper. Connect its Bool input to the output of the Greater Than function and its Nodes input to the "employee" output in the XML Reader.

Now connect the output of the Filter function to the "staff_member" input in the XML Writer. This will ensure that an "employee" element is only mapped if its "second_name" element comes from the second half of the alphabet.

Finally let's make the remaining input and output connections. Remember to map "second_name" to "s_name" - although we have used this value from the source we have not yet instructed the Mapper to map it.

We can now execute the transform by pressing Shift-F5 or the Execute button (![]() ). The transform is applied and the file we selected as output opens in the editor:
). The transform is applied and the file we selected as output opens in the editor:
| Output XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<company> <staff_member since="2008" contract="false"> <f_name>Joe</f_name> <s_name>Simpson</s_name> </staff_member> <staff_member since="2008" contract="false"> <f_name>Lynn</f_name> <s_name>Nicolson</s_name> </staff_member> </company> |
|
The output only contains those "staff_member" elements with surnames from "N" onwards. Most of the Comparator functions are particularly useful when you need to filter or transform your data depending on an unknown range of input values.