Function Name |
Count | ||||
Category |
Aggregate | ||||
Icon |
 |
||||
Description |
Retrieve the number of values within a context | ||||
Inputs |
|
||||
Outputs |
|
||||
Properties |
|
||||
Usage
The Data Mapper Aggregate Count function allows you to retrieve the number of values within specific contexts. The Context input is optional, so you can simply retrieve the count of values in the whole data source by not connecting it. If you do connect the Context input, the count is taken within the specified parent node. To apply the Aggregate Count function, use the following process:
Create a new Data Mapper file, dragging your XML data source and targets into the editor area. For this example we are using sellers_source.xsd, an XML Schema Definition inferred from the following source:
| Source XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<sellers> <salesperson> <name>John Davidson</name> <sales>12800</sales> </salesperson> <salesperson> <name>Jane Johnson</name> <sales>23050</sales> </salesperson> <salesperson> <name>Mark Smith</name> <sales>18200</sales> </salesperson> </sellers> |
|
For our target schema we will be using sellers_target.xsd, inferred from the following XML:
| Target XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<sales_staff> <sales_data type="count">3</sales_data> <sales_assistant seller_name="Ken Jameson"> <amount>34020</amount> </sales_assistant> <sales_assistant seller_name="Lisa Matthews"> <amount>27500</amount> </sales_assistant> <sales_assistant seller_name="Paul Norton"> <amount>23700</amount> </sales_assistant> </sales_staff> |
|
The data models sales for individual salespeople within a retail organisation. Let's assume that, as well as mapping the salespeople and their data, we also want to determine the number of sales figures we are dealing with across all staff members. We will record this in the "sales_data" element together with a String indicating the type of data we are recording as in the target above. Here is the Data Mapper with Source and Target imported:

Drag the Aggregate Count function from the Component Palette into the mapping area:

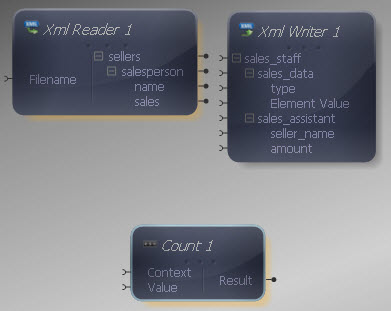
The Count function takes two inputs, representing the value to retrieve the count of and the context in which it should be counted. Both inputs and output of the Count function may be connected to items in the XML Reader/ Writer or other components in the Mapper.
Connect the Context input of the Count function to the "sellers" output in the XML Reader and the Value input to the "sales" output.

This will output the number of sales figures across all sellers. In this case, the effect would be the same if we did not connect the Context input, however if we had categories of sellers, for example in different stores, we would perhaps want to calculate the number of sales figures for each store, in which case the Context input would be different. Connect the Count output to the "Element Value" within the "sales_data" element in the XML Writer.

This will ensure that the "sales_data" element is written out with the number of sales figures inside it each time the data is mapped.
Now we need to define the type of data we are including in the "sales_data" element. Drag a Constant Value from the Data Type section onto the Mapper. Right-click it and choose Show Properties. Choose a String Data Type enter "count" as the Value, or anything else you prefer.

Connect the Constant output to the "type" input in the XML Writer.

Finally let's make the remaining input and output connections. Remember to map "sellers" to "sales_staff" and "sales" to "amount" - although we have used these as references we have not yet mapped them. We do not need to map anything to the "sales_data" element input as the Element Value will ensure the element itself is mapped.

We can now execute the transform by pressing Shift-F5 or the Execute button (![]() ). The transform is applied and the file we selected as output opens in the editor:
). The transform is applied and the file we selected as output opens in the editor:
| Output XML |
Copy Code
|
|---|---|
<sales_staff> <sales_data type="count">3</sales_data> <sales_assistant seller_name="John Davidson"> <amount>12800</amount> </sales_assistant> <sales_assistant seller_name="Jane Johnson"> <amount>23050</amount> </sales_assistant> <sales_assistant seller_name="Mark Smith"> <amount>18200</amount> </sales_assistant> </sales_staff> |
|
The output contains the data values mapped from the source and the number of sales figures, included in the "sales_data" element, together with a String indicating the meaning of the value.